From bba97b225ab6a2c1da199bd0b6136668544d5eac Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
From: "promptless[bot]" <179508745+promptless[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Thu, 5 Feb 2026 18:53:01 +0000
Subject: [PATCH] Add WebSocket streaming tutorial for Serverless
---
docs.json | 1 +
tutorials/serverless/websocket-streaming.mdx | 420 +++++++++++++++++++
2 files changed, 421 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 tutorials/serverless/websocket-streaming.mdx
diff --git a/docs.json b/docs.json
index b15a9105..402a6f9b 100644
--- a/docs.json
+++ b/docs.json
@@ -283,6 +283,7 @@
"group": "Serverless",
"pages": [
"tutorials/serverless/run-your-first",
+ "tutorials/serverless/websocket-streaming",
"tutorials/serverless/comfyui",
"tutorials/serverless/model-caching-text",
"tutorials/serverless/generate-sdxl-turbo",
diff --git a/tutorials/serverless/websocket-streaming.mdx b/tutorials/serverless/websocket-streaming.mdx
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..16747984
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tutorials/serverless/websocket-streaming.mdx
@@ -0,0 +1,420 @@
+---
+title: "Stream data with WebSocket-style streaming"
+sidebarTitle: "WebSocket streaming"
+description: "Build a Serverless endpoint that streams data back to your client using WebSocket-style streaming."
+---
+
+In this tutorial, you'll build a Serverless endpoint that streams data back to your client using WebSocket-style streaming. This approach works well for workloads that process data incrementally—like image processing or text generation—where you want to return partial results as they become available.
+
+You'll create a handler that simulates chunked image processing, deploy it to Runpod Serverless, and build a Python client that receives streamed responses in real time.
+
+## What you'll learn
+
+- Create a streaming handler function that yields incremental results.
+- Deploy a custom worker with streaming enabled.
+- Send requests to your endpoint and receive streamed responses.
+- Process and display streaming output in a Python client.
+
+## Requirements
+
+Before starting, you'll need:
+
+- A Runpod account with credits.
+- A Runpod [API key](/get-started/api-keys).
+- Python 3.9+ installed locally.
+- Docker installed and configured.
+- A Docker Hub account for pushing your worker image.
+
+## Step 1: Set up your development environment
+
+Create a project directory and set up a Python virtual environment:
+
+```bash
+mkdir runpod-base64-stream
+cd runpod-base64-stream
+python -m venv venv
+source venv/bin/activate
+pip install runpod Pillow
+```
+
+## Step 2: Create a streaming handler function
+
+Create a file named `handler.py` with the following code:
+
+```python handler.py
+import runpod
+import base64
+import io
+from PIL import Image
+import time
+
+def process_image_chunk(chunk_data, chunk_number, total_chunks):
+ """
+ Simulate processing a chunk of image data.
+ In a real application, you might do actual image processing here.
+ """
+ return {
+ "chunk_number": chunk_number,
+ "chunk_size": len(chunk_data),
+ "processed_at": time.strftime("%H:%M:%S")
+ }
+
+def generator_handler(job):
+ """
+ Handler that processes a base64 encoded image in chunks and streams results.
+ """
+ job_input = job["input"]
+
+ # Get the base64 string from input
+ base64_string = job_input.get("base64_image")
+ if not base64_string:
+ yield {"error": "No base64_image provided in input"}
+ return
+
+ try:
+ # Decode base64 string
+ image_data = base64.b64decode(base64_string)
+
+ # Open image to validate and get info
+ image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(image_data))
+
+ # Get image info for initial metadata
+ yield {
+ "status": "started",
+ "image_info": {
+ "format": image.format,
+ "size": image.size,
+ "mode": image.mode
+ }
+ }
+
+ # Simulate processing image in chunks
+ # In a real application, you might process different parts of the image
+ chunk_size = len(image_data) // 4 # Process in 4 chunks
+ total_chunks = (len(image_data) + chunk_size - 1) // chunk_size
+
+ for i in range(total_chunks):
+ start_idx = i * chunk_size
+ end_idx = min(start_idx + chunk_size, len(image_data))
+ chunk = image_data[start_idx:end_idx]
+
+ # Process this chunk
+ result = process_image_chunk(chunk, i + 1, total_chunks)
+
+ # Add progress information
+ result["progress"] = f"{i + 1}/{total_chunks}"
+ result["percent_complete"] = ((i + 1) / total_chunks) * 100
+
+ # Stream the result for this chunk
+ yield result
+
+ # Simulate processing time
+ time.sleep(1)
+
+ # Send final completion message
+ yield {
+ "status": "completed",
+ "total_chunks_processed": total_chunks,
+ "final_timestamp": time.strftime("%H:%M:%S")
+ }
+
+ except Exception as e:
+ yield {"error": str(e)}
+
+# Start the serverless function with streaming enabled
+runpod.serverless.start({
+ "handler": generator_handler,
+ "return_aggregate_stream": True
+})
+```
+
+This handler:
+- Accepts a base64-encoded image in the request input.
+- Yields an initial status message with image metadata.
+- Processes the image in chunks, yielding progress updates for each chunk.
+- Sends a final completion message when done.
+
+The key to streaming is using `yield` instead of `return`, and setting `return_aggregate_stream` to `True` when starting the serverless function. This makes the streamed results available via the `/stream` endpoint.
+
+## Step 3: Create a Dockerfile
+
+Create a `Dockerfile` to package your handler:
+
+```dockerfile Dockerfile
+FROM python:3.9-slim
+
+WORKDIR /app
+
+# Install system dependencies for Pillow
+RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
+ libjpeg-dev \
+ zlib1g-dev \
+ && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
+
+COPY requirements.txt .
+RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
+
+COPY handler.py .
+
+CMD [ "python", "-u", "handler.py" ]
+```
+
+Create a `requirements.txt` file:
+
+```txt requirements.txt
+runpod==1.3.0
+Pillow==9.5.0
+```
+
+## Step 4: Build and push your Docker image
+
+Build and push your image to Docker Hub:
+
+```bash
+docker build --platform linux/amd64 -t YOUR_DOCKERHUB_USERNAME/runpod-base64-stream:latest .
+docker push YOUR_DOCKERHUB_USERNAME/runpod-base64-stream:latest
+```
+
+Replace `YOUR_DOCKERHUB_USERNAME` with your actual Docker Hub username.
+
+## Step 5: Create a Serverless endpoint
+
+Deploy your worker to a Serverless endpoint using the Runpod console:
+
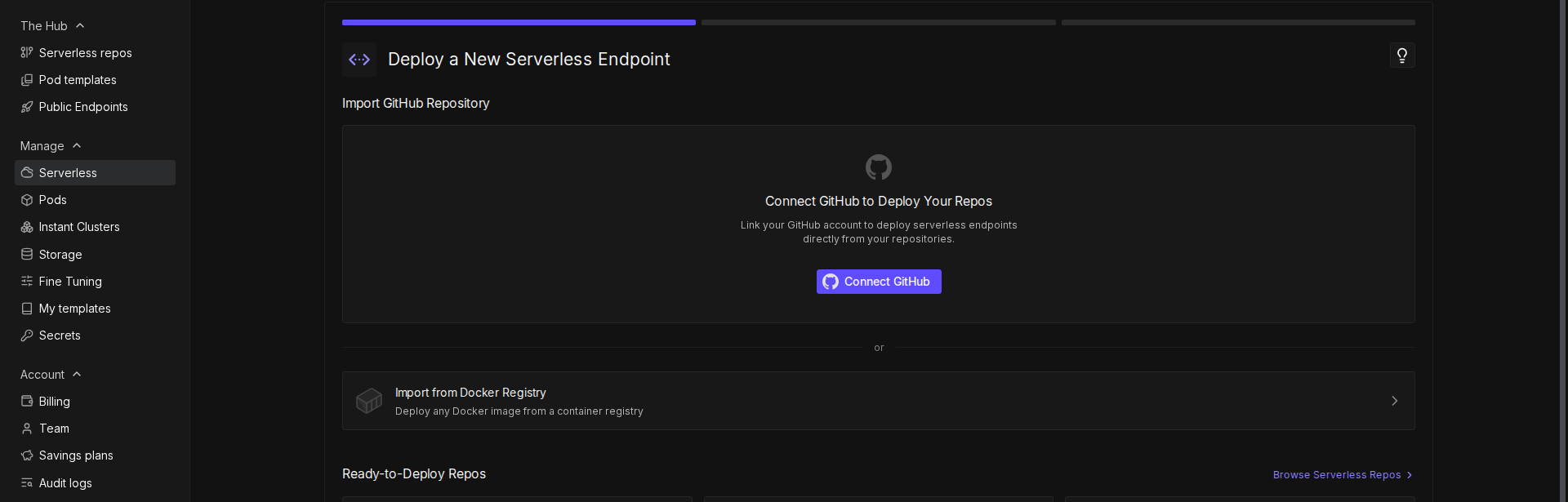
+1. Go to the [Serverless](https://www.runpod.io/console/serverless) section of the Runpod console.
+2. Click **New Endpoint**.
+3. Click **Import from Docker Registry**.
+
+
+  +
+
+4. In the **Container Image** field, enter your Docker image URL (e.g., `docker.io/YOUR_DOCKERHUB_USERNAME/runpod-base64-stream:latest`).
+5. Click **Next**.
+
+
+
+
+
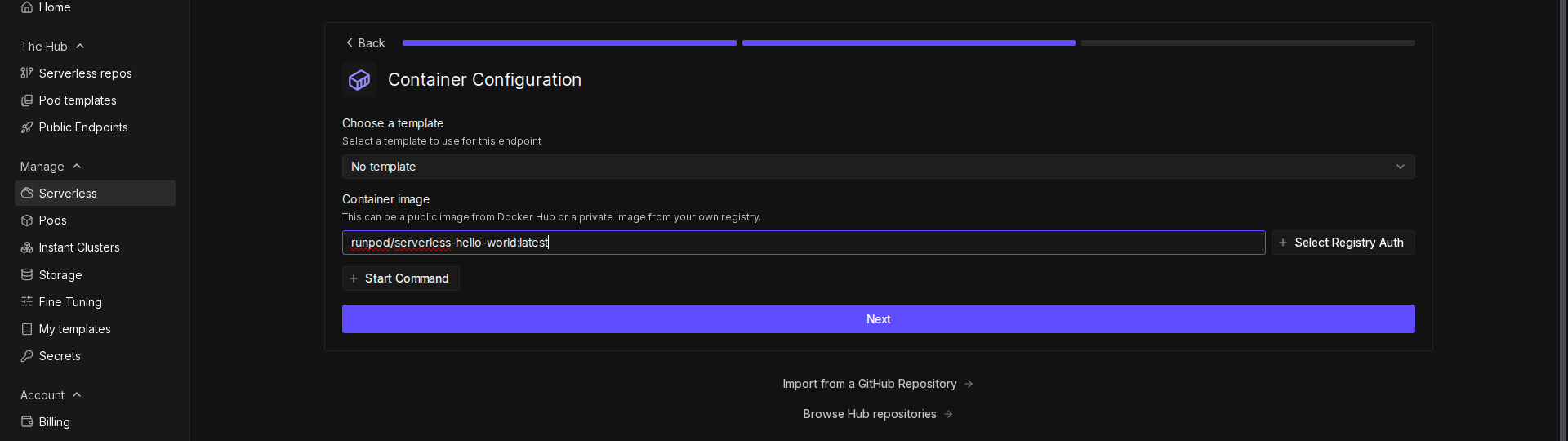
+4. In the **Container Image** field, enter your Docker image URL (e.g., `docker.io/YOUR_DOCKERHUB_USERNAME/runpod-base64-stream:latest`).
+5. Click **Next**.
+
+
+  +
+
+6. Configure your endpoint:
+ - Enter a name for your endpoint, or use the randomly generated name.
+ - Make sure **Endpoint Type** is set to **Queue**.
+ - Under **GPU Configuration**, select **16 GB** GPUs.
+ - Leave the rest of the settings at their defaults.
+
+
+
+
+
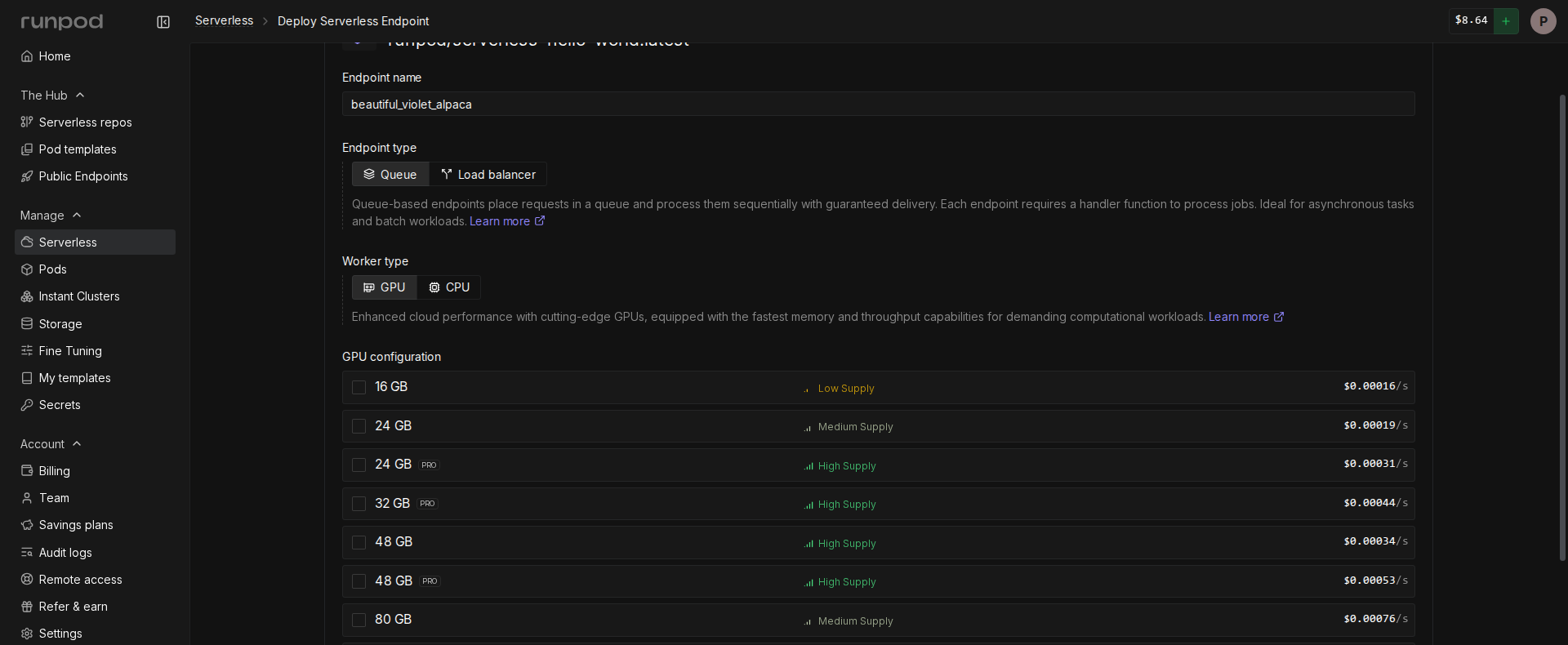
+6. Configure your endpoint:
+ - Enter a name for your endpoint, or use the randomly generated name.
+ - Make sure **Endpoint Type** is set to **Queue**.
+ - Under **GPU Configuration**, select **16 GB** GPUs.
+ - Leave the rest of the settings at their defaults.
+
+
+  +
+
+7. Click **Deploy Endpoint**.
+
+Once deployed, note the **Endpoint ID** from the endpoint details page—you'll need it in the next step.
+
+## Step 6: Test the endpoint
+
+Create a file named `test_endpoint.py` to test your streaming endpoint:
+
+```python test_endpoint.py
+import requests
+import json
+import time
+import base64
+from PIL import Image
+import io
+import os
+
+API_KEY = "YOUR_RUNPOD_API_KEY"
+ENDPOINT_ID = "YOUR_ENDPOINT_ID"
+
+# Set up the output directory for saving images
+OUTPUT_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "output_images")
+
+# Create the output directory if it doesn't exist
+if not os.path.exists(OUTPUT_DIR):
+ os.makedirs(OUTPUT_DIR)
+ print(f"Created output directory: {OUTPUT_DIR}")
+
+def create_test_image():
+ """
+ Creates a test image and converts it to base64 format.
+
+ Returns:
+ str: The image encoded as a base64 string
+ """
+ # Create a new 100x100 pixel image with a red background
+ img = Image.new('RGB', (100, 100), color='red')
+
+ # Create a bytes buffer to hold the image data
+ img_byte_arr = io.BytesIO()
+
+ # Save the image to the buffer in PNG format
+ img.save(img_byte_arr, format='PNG')
+
+ # Get the byte data from the buffer
+ img_byte_arr = img_byte_arr.getvalue()
+
+ # Save a copy of the input image to disk
+ input_path = os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, 'test_image_input.png')
+ img.save(input_path)
+ print(f"Saved input test image as: {input_path}")
+
+ # Convert the image bytes to base64 string and return it
+ return base64.b64encode(img_byte_arr).decode('utf-8')
+
+def save_base64_image(base64_string, filename):
+ """
+ Converts a base64 string back to an image and saves it to disk.
+
+ Args:
+ base64_string (str): The image data as a base64 string
+ filename (str): The name to give the saved file
+ """
+ try:
+ # Create the full path where the file will be saved
+ output_path = os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, filename)
+
+ # Convert the base64 string back to bytes
+ image_data = base64.b64decode(base64_string)
+
+ # Create an image from the bytes
+ image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(image_data))
+
+ # Save the image as a PNG file
+ image.save(output_path, 'PNG')
+ print(f"Saved processed image as: {output_path}")
+
+ return True
+ except Exception as e:
+ print(f"Error saving image: {str(e)}")
+ return False
+
+# Set up the API endpoint URLs
+run_url = f"https://api.runpod.ai/v2/{ENDPOINT_ID}/run"
+
+# Set up the headers for the API request
+headers = {
+ "Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}",
+ "Content-Type": "application/json"
+}
+
+# Print a redacted version of the authorization header for debugging
+print("Using Authorization header:", headers["Authorization"][:10] + "...")
+
+# Create the test image and get its base64 representation
+base64_image = create_test_image()
+
+# Create the payload for our API request
+payload = {
+ "input": {
+ "base64_image": base64_image
+ }
+}
+
+# Send the initial request to start the job
+print("\nSending request to:", run_url)
+response = requests.post(run_url, headers=headers, json=payload)
+
+# Print debug information about the response
+print("Status Code:", response.status_code)
+
+# Check for authentication errors
+if response.status_code == 401:
+ print("\nAuthentication Error: Please check your API key")
+ exit()
+
+try:
+ # Parse the JSON response
+ job_status = response.json()
+ job_id = job_status["id"]
+ print(f"\nStarted job: {job_id}")
+
+ # Set up the streaming URL for getting results
+ stream_url = f"https://api.runpod.ai/v2/{ENDPOINT_ID}/stream/{job_id}"
+
+ # Keep checking for results until the job is done
+ while True:
+ # Get the current status of the job
+ stream_response = requests.get(stream_url, headers=headers)
+ stream_data = stream_response.json()
+
+ # Check if the job is completed
+ if stream_data["status"] == "COMPLETED":
+ print("\nJob completed!")
+ break
+
+ # Check if the job is still running and has new data
+ elif stream_data["status"] == "IN_PROGRESS" and stream_data.get("stream"):
+ # Process each piece of output data
+ for output in stream_data["stream"]:
+ print(f"Received: {json.dumps(output, indent=2)}")
+
+ # If we received a processed image, save it
+ if "processed_image" in output:
+ filename = f"output_image_{output.get('chunk_number', 'final')}.png"
+ save_base64_image(output["processed_image"], filename)
+
+ # Check if the job failed
+ elif stream_data["status"] == "FAILED":
+ print("\nJob failed!")
+ print(stream_data.get("error", "No error message provided"))
+ break
+
+ # Wait a bit before checking again
+ time.sleep(0.5)
+
+except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
+ print("\nError decoding JSON response:", str(e))
+except KeyError as e:
+ print("\nError accessing response data:", str(e))
+ print("Full response:", job_status)
+except Exception as e:
+ print("\nUnexpected error:", str(e))
+```
+
+
+Replace `YOUR_RUNPOD_API_KEY` and `YOUR_ENDPOINT_ID` with your actual API key and endpoint ID before running the script.
+
+
+Run the test script:
+
+```bash
+python test_endpoint.py
+```
+
+You should see output similar to this:
+
+```text
+Started job: 123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000
+Received: {
+ "status": "started",
+ "image_info": {
+ "format": "PNG",
+ "size": [100, 100],
+ "mode": "RGB"
+ }
+}
+Received: {
+ "chunk_number": 1,
+ "chunk_size": 2500,
+ "processed_at": "14:30:45",
+ "progress": "1/4",
+ "percent_complete": 25.0
+}
+...
+Received: {
+ "status": "completed",
+ "total_chunks_processed": 4,
+ "final_timestamp": "14:30:48"
+}
+Job completed!
+```
+
+The test script sends a base64-encoded image to your endpoint, then polls the `/stream` endpoint to receive incremental results as they become available.
+
+## Next steps
+
+Now that you've built a streaming endpoint, explore these related topics:
+
+- Learn more about [streaming handlers](/serverless/workers/handler-functions#streaming-handlers) and handler types.
+- Explore the [/stream operation](/serverless/endpoints/send-requests#stream) for receiving streamed results.
+- Try building a [concurrent handler](/serverless/workers/concurrent-handler) to process multiple requests simultaneously.
+
+
+7. Click **Deploy Endpoint**.
+
+Once deployed, note the **Endpoint ID** from the endpoint details page—you'll need it in the next step.
+
+## Step 6: Test the endpoint
+
+Create a file named `test_endpoint.py` to test your streaming endpoint:
+
+```python test_endpoint.py
+import requests
+import json
+import time
+import base64
+from PIL import Image
+import io
+import os
+
+API_KEY = "YOUR_RUNPOD_API_KEY"
+ENDPOINT_ID = "YOUR_ENDPOINT_ID"
+
+# Set up the output directory for saving images
+OUTPUT_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "output_images")
+
+# Create the output directory if it doesn't exist
+if not os.path.exists(OUTPUT_DIR):
+ os.makedirs(OUTPUT_DIR)
+ print(f"Created output directory: {OUTPUT_DIR}")
+
+def create_test_image():
+ """
+ Creates a test image and converts it to base64 format.
+
+ Returns:
+ str: The image encoded as a base64 string
+ """
+ # Create a new 100x100 pixel image with a red background
+ img = Image.new('RGB', (100, 100), color='red')
+
+ # Create a bytes buffer to hold the image data
+ img_byte_arr = io.BytesIO()
+
+ # Save the image to the buffer in PNG format
+ img.save(img_byte_arr, format='PNG')
+
+ # Get the byte data from the buffer
+ img_byte_arr = img_byte_arr.getvalue()
+
+ # Save a copy of the input image to disk
+ input_path = os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, 'test_image_input.png')
+ img.save(input_path)
+ print(f"Saved input test image as: {input_path}")
+
+ # Convert the image bytes to base64 string and return it
+ return base64.b64encode(img_byte_arr).decode('utf-8')
+
+def save_base64_image(base64_string, filename):
+ """
+ Converts a base64 string back to an image and saves it to disk.
+
+ Args:
+ base64_string (str): The image data as a base64 string
+ filename (str): The name to give the saved file
+ """
+ try:
+ # Create the full path where the file will be saved
+ output_path = os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, filename)
+
+ # Convert the base64 string back to bytes
+ image_data = base64.b64decode(base64_string)
+
+ # Create an image from the bytes
+ image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(image_data))
+
+ # Save the image as a PNG file
+ image.save(output_path, 'PNG')
+ print(f"Saved processed image as: {output_path}")
+
+ return True
+ except Exception as e:
+ print(f"Error saving image: {str(e)}")
+ return False
+
+# Set up the API endpoint URLs
+run_url = f"https://api.runpod.ai/v2/{ENDPOINT_ID}/run"
+
+# Set up the headers for the API request
+headers = {
+ "Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}",
+ "Content-Type": "application/json"
+}
+
+# Print a redacted version of the authorization header for debugging
+print("Using Authorization header:", headers["Authorization"][:10] + "...")
+
+# Create the test image and get its base64 representation
+base64_image = create_test_image()
+
+# Create the payload for our API request
+payload = {
+ "input": {
+ "base64_image": base64_image
+ }
+}
+
+# Send the initial request to start the job
+print("\nSending request to:", run_url)
+response = requests.post(run_url, headers=headers, json=payload)
+
+# Print debug information about the response
+print("Status Code:", response.status_code)
+
+# Check for authentication errors
+if response.status_code == 401:
+ print("\nAuthentication Error: Please check your API key")
+ exit()
+
+try:
+ # Parse the JSON response
+ job_status = response.json()
+ job_id = job_status["id"]
+ print(f"\nStarted job: {job_id}")
+
+ # Set up the streaming URL for getting results
+ stream_url = f"https://api.runpod.ai/v2/{ENDPOINT_ID}/stream/{job_id}"
+
+ # Keep checking for results until the job is done
+ while True:
+ # Get the current status of the job
+ stream_response = requests.get(stream_url, headers=headers)
+ stream_data = stream_response.json()
+
+ # Check if the job is completed
+ if stream_data["status"] == "COMPLETED":
+ print("\nJob completed!")
+ break
+
+ # Check if the job is still running and has new data
+ elif stream_data["status"] == "IN_PROGRESS" and stream_data.get("stream"):
+ # Process each piece of output data
+ for output in stream_data["stream"]:
+ print(f"Received: {json.dumps(output, indent=2)}")
+
+ # If we received a processed image, save it
+ if "processed_image" in output:
+ filename = f"output_image_{output.get('chunk_number', 'final')}.png"
+ save_base64_image(output["processed_image"], filename)
+
+ # Check if the job failed
+ elif stream_data["status"] == "FAILED":
+ print("\nJob failed!")
+ print(stream_data.get("error", "No error message provided"))
+ break
+
+ # Wait a bit before checking again
+ time.sleep(0.5)
+
+except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
+ print("\nError decoding JSON response:", str(e))
+except KeyError as e:
+ print("\nError accessing response data:", str(e))
+ print("Full response:", job_status)
+except Exception as e:
+ print("\nUnexpected error:", str(e))
+```
+
+
+Replace `YOUR_RUNPOD_API_KEY` and `YOUR_ENDPOINT_ID` with your actual API key and endpoint ID before running the script.
+
+
+Run the test script:
+
+```bash
+python test_endpoint.py
+```
+
+You should see output similar to this:
+
+```text
+Started job: 123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000
+Received: {
+ "status": "started",
+ "image_info": {
+ "format": "PNG",
+ "size": [100, 100],
+ "mode": "RGB"
+ }
+}
+Received: {
+ "chunk_number": 1,
+ "chunk_size": 2500,
+ "processed_at": "14:30:45",
+ "progress": "1/4",
+ "percent_complete": 25.0
+}
+...
+Received: {
+ "status": "completed",
+ "total_chunks_processed": 4,
+ "final_timestamp": "14:30:48"
+}
+Job completed!
+```
+
+The test script sends a base64-encoded image to your endpoint, then polls the `/stream` endpoint to receive incremental results as they become available.
+
+## Next steps
+
+Now that you've built a streaming endpoint, explore these related topics:
+
+- Learn more about [streaming handlers](/serverless/workers/handler-functions#streaming-handlers) and handler types.
+- Explore the [/stream operation](/serverless/endpoints/send-requests#stream) for receiving streamed results.
+- Try building a [concurrent handler](/serverless/workers/concurrent-handler) to process multiple requests simultaneously.
 +
+
+4. In the **Container Image** field, enter your Docker image URL (e.g., `docker.io/YOUR_DOCKERHUB_USERNAME/runpod-base64-stream:latest`).
+5. Click **Next**.
+
+
+
+
+
+4. In the **Container Image** field, enter your Docker image URL (e.g., `docker.io/YOUR_DOCKERHUB_USERNAME/runpod-base64-stream:latest`).
+5. Click **Next**.
+
+
+  +
+
+6. Configure your endpoint:
+ - Enter a name for your endpoint, or use the randomly generated name.
+ - Make sure **Endpoint Type** is set to **Queue**.
+ - Under **GPU Configuration**, select **16 GB** GPUs.
+ - Leave the rest of the settings at their defaults.
+
+
+
+
+
+6. Configure your endpoint:
+ - Enter a name for your endpoint, or use the randomly generated name.
+ - Make sure **Endpoint Type** is set to **Queue**.
+ - Under **GPU Configuration**, select **16 GB** GPUs.
+ - Leave the rest of the settings at their defaults.
+
+
+  +
+
+7. Click **Deploy Endpoint**.
+
+Once deployed, note the **Endpoint ID** from the endpoint details page—you'll need it in the next step.
+
+## Step 6: Test the endpoint
+
+Create a file named `test_endpoint.py` to test your streaming endpoint:
+
+```python test_endpoint.py
+import requests
+import json
+import time
+import base64
+from PIL import Image
+import io
+import os
+
+API_KEY = "YOUR_RUNPOD_API_KEY"
+ENDPOINT_ID = "YOUR_ENDPOINT_ID"
+
+# Set up the output directory for saving images
+OUTPUT_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "output_images")
+
+# Create the output directory if it doesn't exist
+if not os.path.exists(OUTPUT_DIR):
+ os.makedirs(OUTPUT_DIR)
+ print(f"Created output directory: {OUTPUT_DIR}")
+
+def create_test_image():
+ """
+ Creates a test image and converts it to base64 format.
+
+ Returns:
+ str: The image encoded as a base64 string
+ """
+ # Create a new 100x100 pixel image with a red background
+ img = Image.new('RGB', (100, 100), color='red')
+
+ # Create a bytes buffer to hold the image data
+ img_byte_arr = io.BytesIO()
+
+ # Save the image to the buffer in PNG format
+ img.save(img_byte_arr, format='PNG')
+
+ # Get the byte data from the buffer
+ img_byte_arr = img_byte_arr.getvalue()
+
+ # Save a copy of the input image to disk
+ input_path = os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, 'test_image_input.png')
+ img.save(input_path)
+ print(f"Saved input test image as: {input_path}")
+
+ # Convert the image bytes to base64 string and return it
+ return base64.b64encode(img_byte_arr).decode('utf-8')
+
+def save_base64_image(base64_string, filename):
+ """
+ Converts a base64 string back to an image and saves it to disk.
+
+ Args:
+ base64_string (str): The image data as a base64 string
+ filename (str): The name to give the saved file
+ """
+ try:
+ # Create the full path where the file will be saved
+ output_path = os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, filename)
+
+ # Convert the base64 string back to bytes
+ image_data = base64.b64decode(base64_string)
+
+ # Create an image from the bytes
+ image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(image_data))
+
+ # Save the image as a PNG file
+ image.save(output_path, 'PNG')
+ print(f"Saved processed image as: {output_path}")
+
+ return True
+ except Exception as e:
+ print(f"Error saving image: {str(e)}")
+ return False
+
+# Set up the API endpoint URLs
+run_url = f"https://api.runpod.ai/v2/{ENDPOINT_ID}/run"
+
+# Set up the headers for the API request
+headers = {
+ "Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}",
+ "Content-Type": "application/json"
+}
+
+# Print a redacted version of the authorization header for debugging
+print("Using Authorization header:", headers["Authorization"][:10] + "...")
+
+# Create the test image and get its base64 representation
+base64_image = create_test_image()
+
+# Create the payload for our API request
+payload = {
+ "input": {
+ "base64_image": base64_image
+ }
+}
+
+# Send the initial request to start the job
+print("\nSending request to:", run_url)
+response = requests.post(run_url, headers=headers, json=payload)
+
+# Print debug information about the response
+print("Status Code:", response.status_code)
+
+# Check for authentication errors
+if response.status_code == 401:
+ print("\nAuthentication Error: Please check your API key")
+ exit()
+
+try:
+ # Parse the JSON response
+ job_status = response.json()
+ job_id = job_status["id"]
+ print(f"\nStarted job: {job_id}")
+
+ # Set up the streaming URL for getting results
+ stream_url = f"https://api.runpod.ai/v2/{ENDPOINT_ID}/stream/{job_id}"
+
+ # Keep checking for results until the job is done
+ while True:
+ # Get the current status of the job
+ stream_response = requests.get(stream_url, headers=headers)
+ stream_data = stream_response.json()
+
+ # Check if the job is completed
+ if stream_data["status"] == "COMPLETED":
+ print("\nJob completed!")
+ break
+
+ # Check if the job is still running and has new data
+ elif stream_data["status"] == "IN_PROGRESS" and stream_data.get("stream"):
+ # Process each piece of output data
+ for output in stream_data["stream"]:
+ print(f"Received: {json.dumps(output, indent=2)}")
+
+ # If we received a processed image, save it
+ if "processed_image" in output:
+ filename = f"output_image_{output.get('chunk_number', 'final')}.png"
+ save_base64_image(output["processed_image"], filename)
+
+ # Check if the job failed
+ elif stream_data["status"] == "FAILED":
+ print("\nJob failed!")
+ print(stream_data.get("error", "No error message provided"))
+ break
+
+ # Wait a bit before checking again
+ time.sleep(0.5)
+
+except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
+ print("\nError decoding JSON response:", str(e))
+except KeyError as e:
+ print("\nError accessing response data:", str(e))
+ print("Full response:", job_status)
+except Exception as e:
+ print("\nUnexpected error:", str(e))
+```
+
+
+
+
+7. Click **Deploy Endpoint**.
+
+Once deployed, note the **Endpoint ID** from the endpoint details page—you'll need it in the next step.
+
+## Step 6: Test the endpoint
+
+Create a file named `test_endpoint.py` to test your streaming endpoint:
+
+```python test_endpoint.py
+import requests
+import json
+import time
+import base64
+from PIL import Image
+import io
+import os
+
+API_KEY = "YOUR_RUNPOD_API_KEY"
+ENDPOINT_ID = "YOUR_ENDPOINT_ID"
+
+# Set up the output directory for saving images
+OUTPUT_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "output_images")
+
+# Create the output directory if it doesn't exist
+if not os.path.exists(OUTPUT_DIR):
+ os.makedirs(OUTPUT_DIR)
+ print(f"Created output directory: {OUTPUT_DIR}")
+
+def create_test_image():
+ """
+ Creates a test image and converts it to base64 format.
+
+ Returns:
+ str: The image encoded as a base64 string
+ """
+ # Create a new 100x100 pixel image with a red background
+ img = Image.new('RGB', (100, 100), color='red')
+
+ # Create a bytes buffer to hold the image data
+ img_byte_arr = io.BytesIO()
+
+ # Save the image to the buffer in PNG format
+ img.save(img_byte_arr, format='PNG')
+
+ # Get the byte data from the buffer
+ img_byte_arr = img_byte_arr.getvalue()
+
+ # Save a copy of the input image to disk
+ input_path = os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, 'test_image_input.png')
+ img.save(input_path)
+ print(f"Saved input test image as: {input_path}")
+
+ # Convert the image bytes to base64 string and return it
+ return base64.b64encode(img_byte_arr).decode('utf-8')
+
+def save_base64_image(base64_string, filename):
+ """
+ Converts a base64 string back to an image and saves it to disk.
+
+ Args:
+ base64_string (str): The image data as a base64 string
+ filename (str): The name to give the saved file
+ """
+ try:
+ # Create the full path where the file will be saved
+ output_path = os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, filename)
+
+ # Convert the base64 string back to bytes
+ image_data = base64.b64decode(base64_string)
+
+ # Create an image from the bytes
+ image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(image_data))
+
+ # Save the image as a PNG file
+ image.save(output_path, 'PNG')
+ print(f"Saved processed image as: {output_path}")
+
+ return True
+ except Exception as e:
+ print(f"Error saving image: {str(e)}")
+ return False
+
+# Set up the API endpoint URLs
+run_url = f"https://api.runpod.ai/v2/{ENDPOINT_ID}/run"
+
+# Set up the headers for the API request
+headers = {
+ "Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}",
+ "Content-Type": "application/json"
+}
+
+# Print a redacted version of the authorization header for debugging
+print("Using Authorization header:", headers["Authorization"][:10] + "...")
+
+# Create the test image and get its base64 representation
+base64_image = create_test_image()
+
+# Create the payload for our API request
+payload = {
+ "input": {
+ "base64_image": base64_image
+ }
+}
+
+# Send the initial request to start the job
+print("\nSending request to:", run_url)
+response = requests.post(run_url, headers=headers, json=payload)
+
+# Print debug information about the response
+print("Status Code:", response.status_code)
+
+# Check for authentication errors
+if response.status_code == 401:
+ print("\nAuthentication Error: Please check your API key")
+ exit()
+
+try:
+ # Parse the JSON response
+ job_status = response.json()
+ job_id = job_status["id"]
+ print(f"\nStarted job: {job_id}")
+
+ # Set up the streaming URL for getting results
+ stream_url = f"https://api.runpod.ai/v2/{ENDPOINT_ID}/stream/{job_id}"
+
+ # Keep checking for results until the job is done
+ while True:
+ # Get the current status of the job
+ stream_response = requests.get(stream_url, headers=headers)
+ stream_data = stream_response.json()
+
+ # Check if the job is completed
+ if stream_data["status"] == "COMPLETED":
+ print("\nJob completed!")
+ break
+
+ # Check if the job is still running and has new data
+ elif stream_data["status"] == "IN_PROGRESS" and stream_data.get("stream"):
+ # Process each piece of output data
+ for output in stream_data["stream"]:
+ print(f"Received: {json.dumps(output, indent=2)}")
+
+ # If we received a processed image, save it
+ if "processed_image" in output:
+ filename = f"output_image_{output.get('chunk_number', 'final')}.png"
+ save_base64_image(output["processed_image"], filename)
+
+ # Check if the job failed
+ elif stream_data["status"] == "FAILED":
+ print("\nJob failed!")
+ print(stream_data.get("error", "No error message provided"))
+ break
+
+ # Wait a bit before checking again
+ time.sleep(0.5)
+
+except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
+ print("\nError decoding JSON response:", str(e))
+except KeyError as e:
+ print("\nError accessing response data:", str(e))
+ print("Full response:", job_status)
+except Exception as e:
+ print("\nUnexpected error:", str(e))
+```
+
+